GLOBHE is a leading provider of drone data solutions, offering a range of services that enable businesses and organizations to collect, analyze, and leverage data captured by drones. Here are all the drone data that GLOBHE can provide:
Let's dive into each product category:
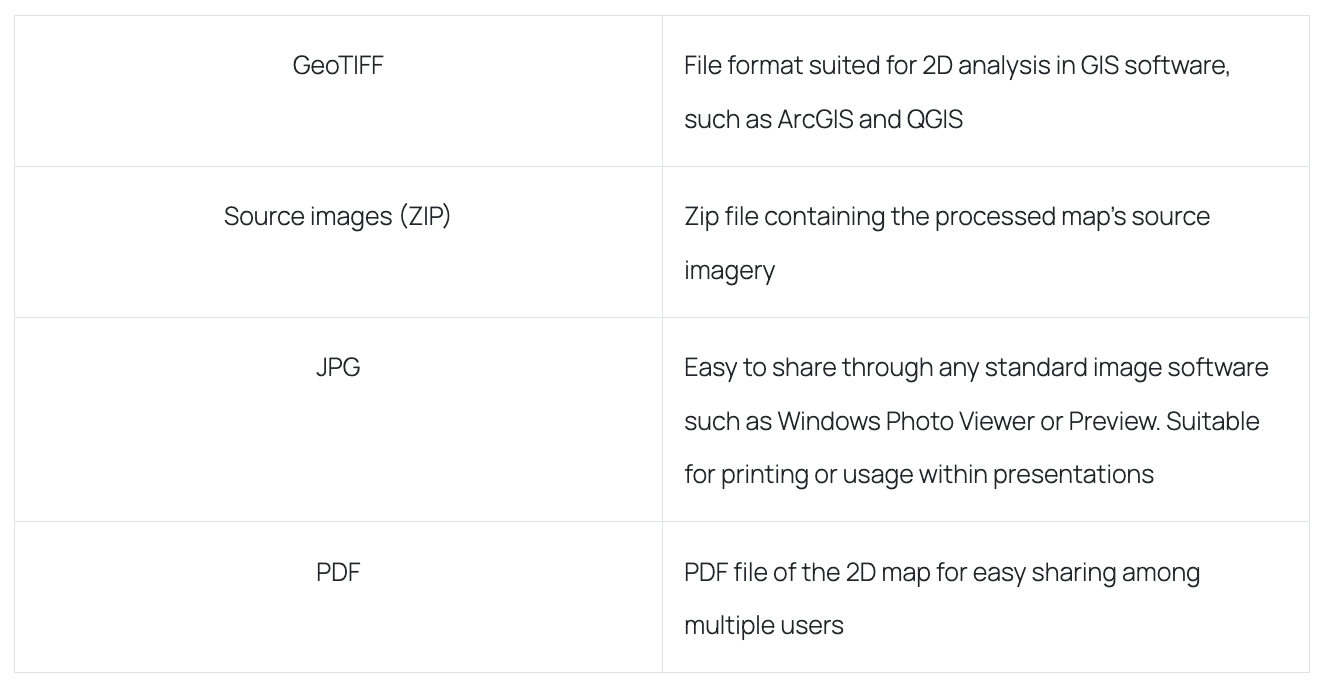
2D Orthomosaic Map
The drones capture individual images, which are then merged to form a high-quality 2D orthomosaic map. This 2D map has various applications across different industries, such as construction and infrastructure, and can be used with all modeling and GIS software. Depending on the capture settings, the resolution of the map can be as high as a few millimeters per pixel. You can zoom in and rotate the map to observe the high-resolution images, and the advantages they offer when compared to satellite imagery.
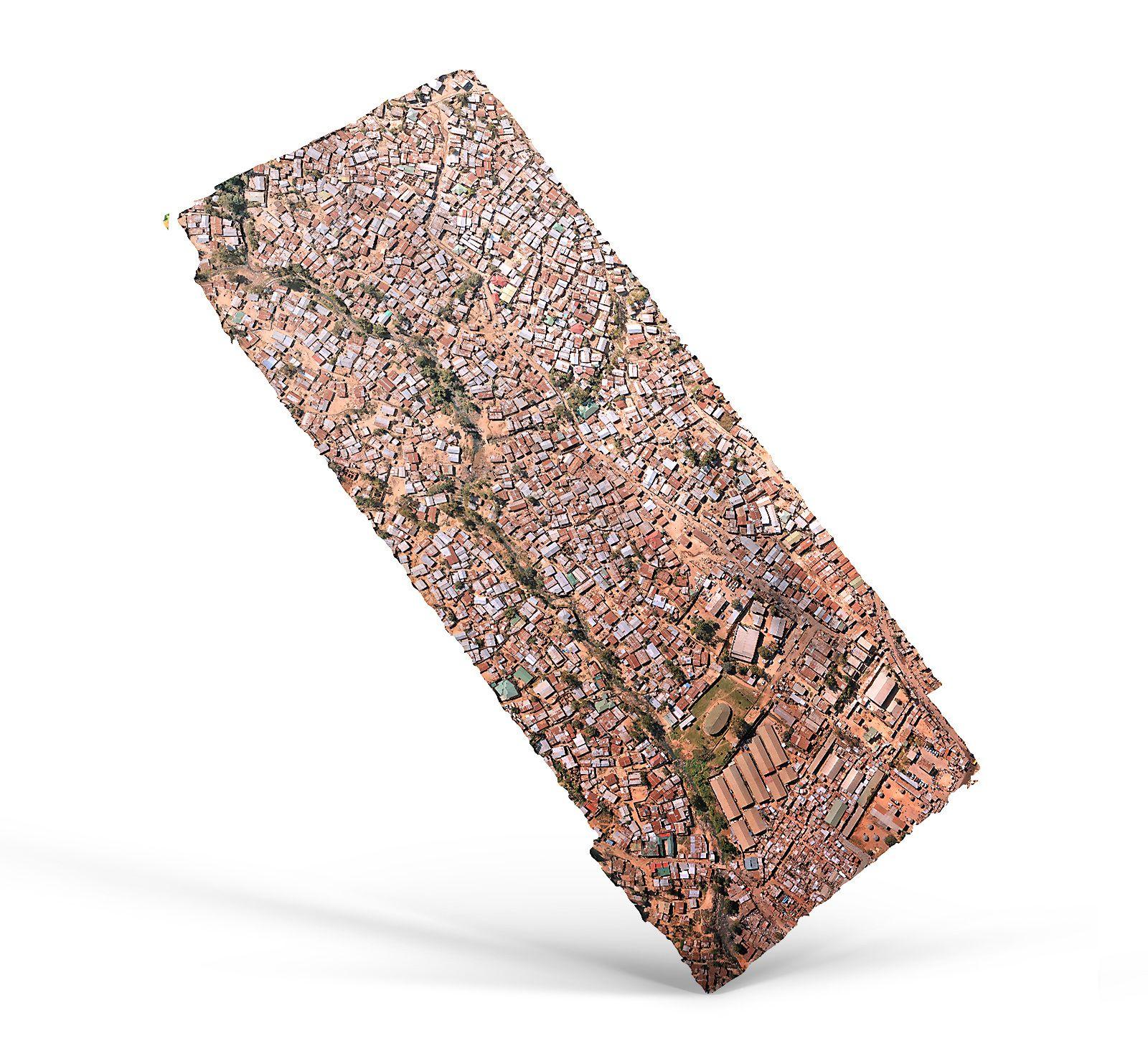

Examples of applications:
In the construction industry, to provide accurate and detailed site surveys, monitor construction progress, and aid in project management and planning.
In agriculture, to monitor crop health and growth, detect potential issues like pest infestations, and support precision farming techniques.
2D Orthomosaic Maps can be used in environmental management to monitor and assess changes in land use, detect potential threats to habitats and ecosystems, and guide decisions regarding conservation and restoration.
In real estate, to provide detailed visualizations of properties and surrounding areas, helping buyers and sellers make informed decisions.
How it is delivered:
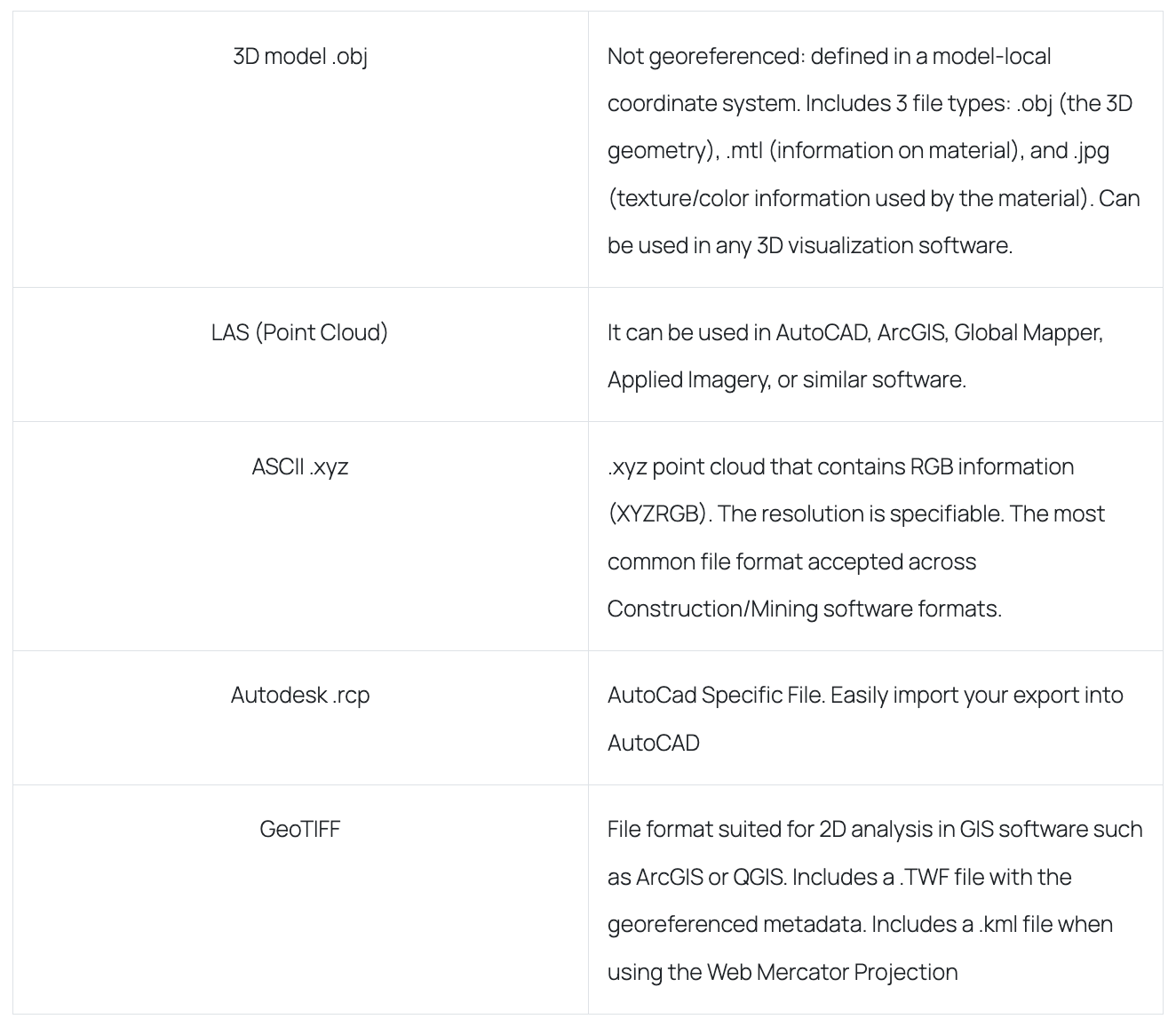
3D model or point cloud
Just like with orthomosaic maps, drone images can be combined to generate a high-resolution 3D model, represented by either a 3D mesh surface or a point cloud. The latter is a 3D representation consisting of thousands or even millions of georeferenced points. Point clouds offer detailed information and enable you to create an interactive 3D model with real-world imagery, which can be easily modified using 3D modeling software. Additionally, point clouds can be utilized to create digital models of structures for CAD and BIM-related tasks, which are integral to modern construction practices.
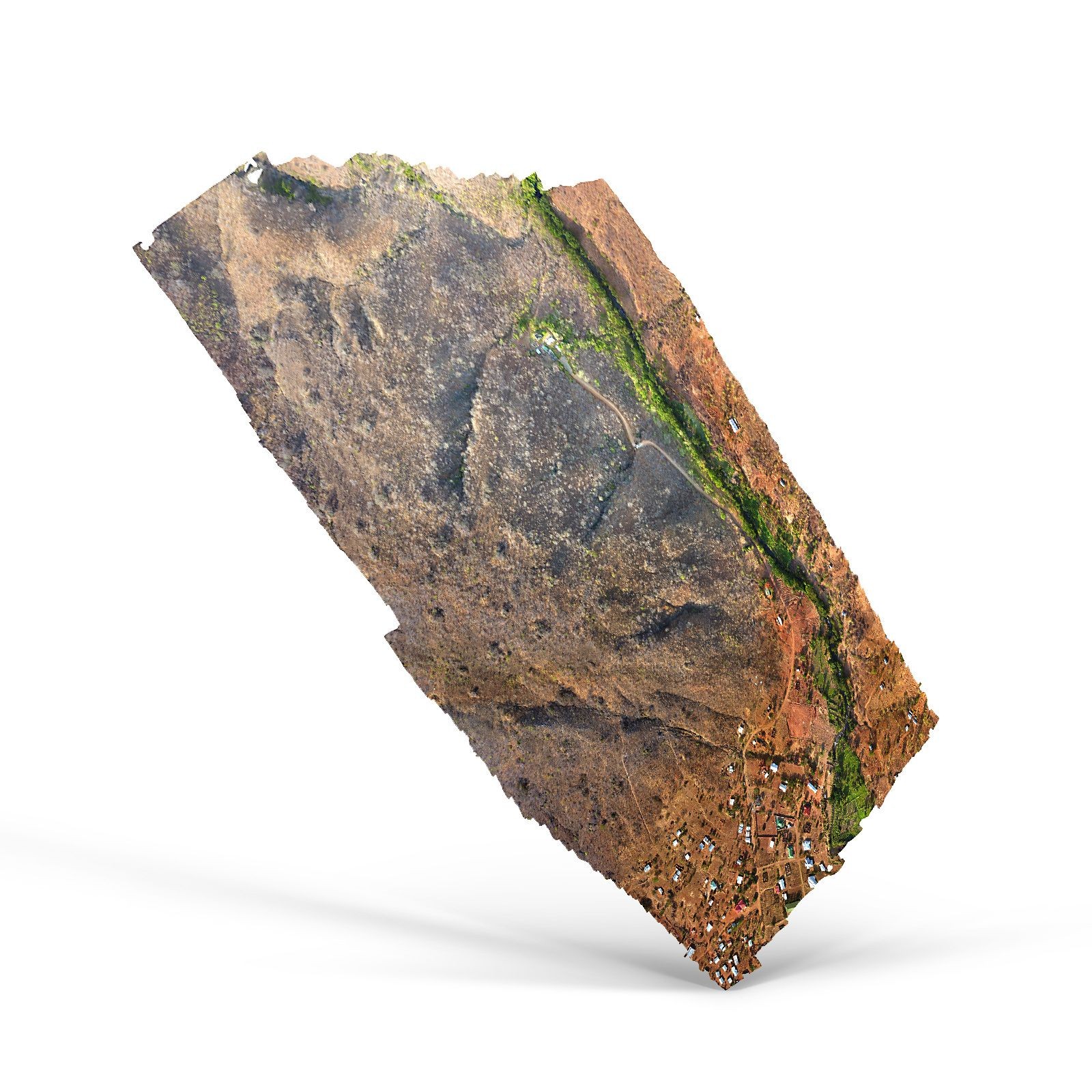

Examples of applications:
3D models and point clouds are used in the energy industry for oil and gas exploration, renewable energy site planning, and pipeline inspection.
In architecture and construction, they are used to create building designs, visualize construction plans, and assess the safety and structural integrity of buildings.
In surveying and mapping, 3D models and point clouds are used to create accurate and detailed maps of landscapes, buildings, and other structures.
In archaeology, 3D models are used to analyze excavation sites and create digital reconstructions of ancient structures.
How they are delivered:
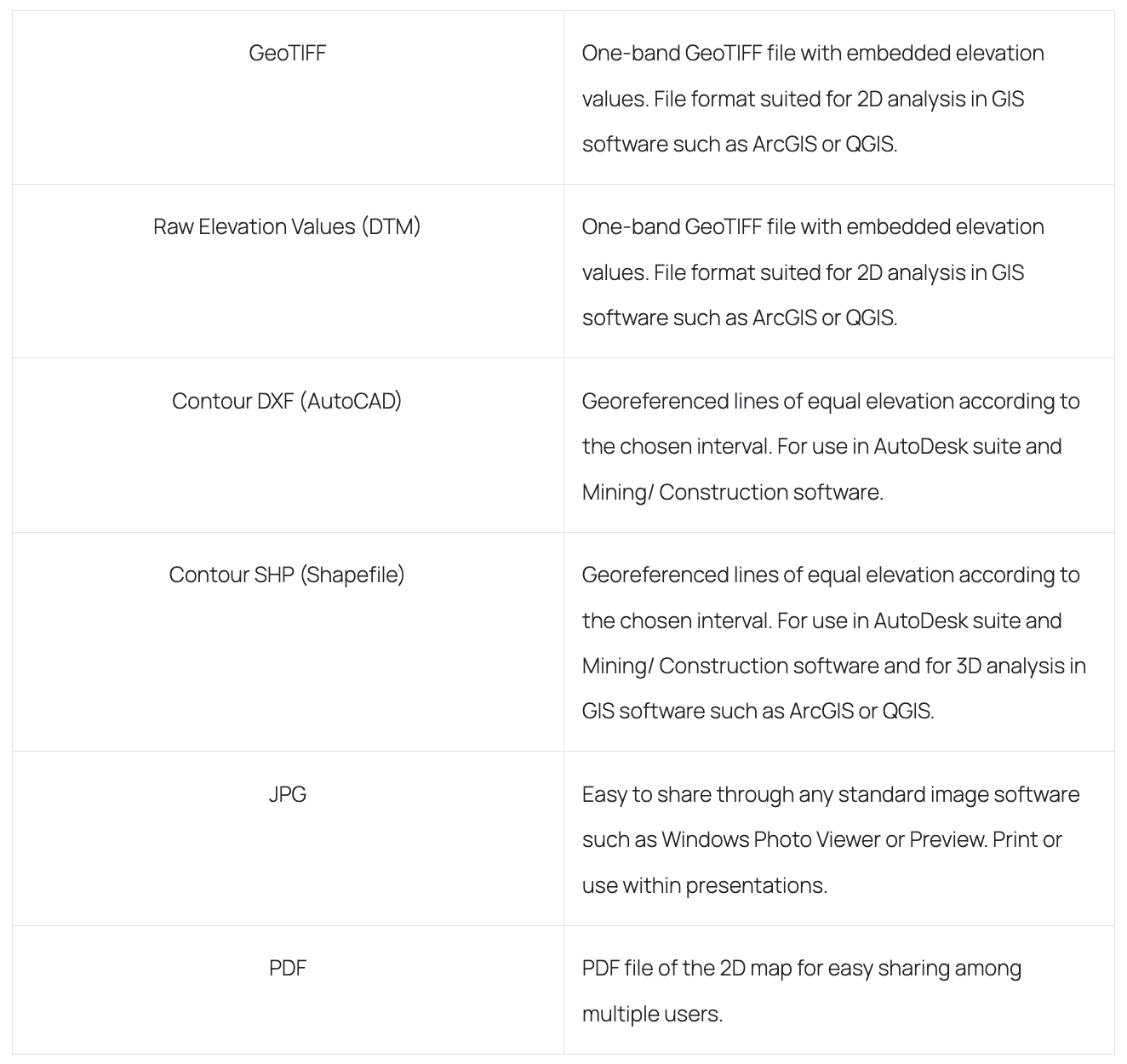
Digital Terrain Model
A Digital Terrain Model (DTM) or terrain surface map displays the ground surface without any objects depicted. Depending on the drone settings, the resolution of these digital elevation models (DEMs) can be as precise as a few centimeters. You can zoom in and rotate this map to observe the offered high-resolution model.
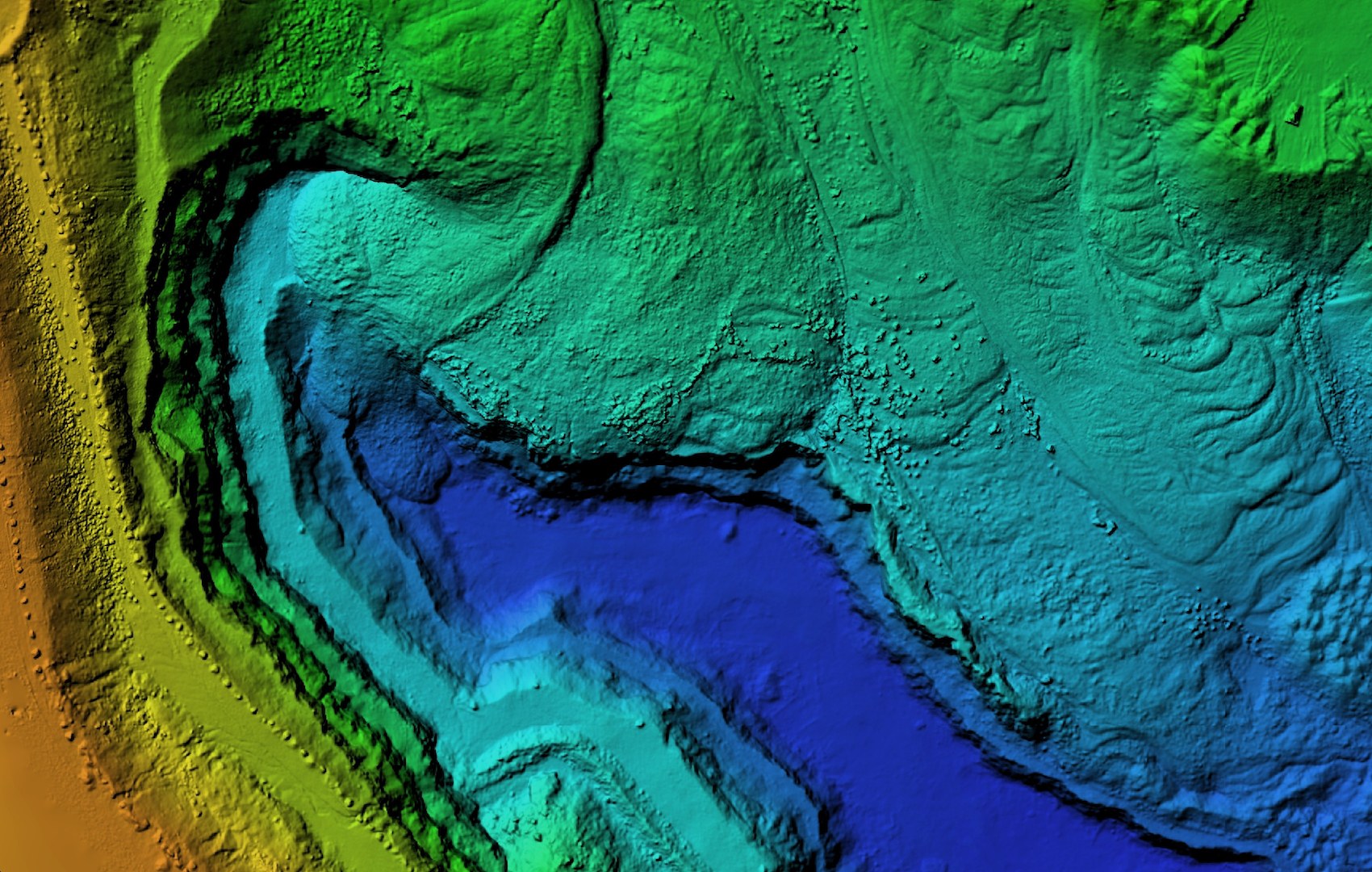
Examples of applications:
A DTM can be used in surveying and mapping to create accurate 3D models of the terrain, providing valuable data for engineering and construction projects.
In urban planning, to create accurate models of urban environments, aiding in the development of infrastructure, transportation, and green spaces.
In the infrastructure industry, to assess the suitability of the terrain for construction projects, such as roads, bridges, and pipelines. It can also be used to detect potential hazards, such as landslides and erosion.
In disaster management, to assess the extent of damage caused by natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, and landslides.
How it is delivered:
Digital Surface Model
A Digital Surface Model (DSM) captured by a drone shows the height data of all surfaces that are captured, including trees, equipment, and other structures. It differs from the digital terrain model, as it depicts objects and vegetation. Depending on the mission configuration, the resolution can be as high as 1 cm. Additionally, the data obtained can be utilized to make precise volumetric calculations from these elevation maps.
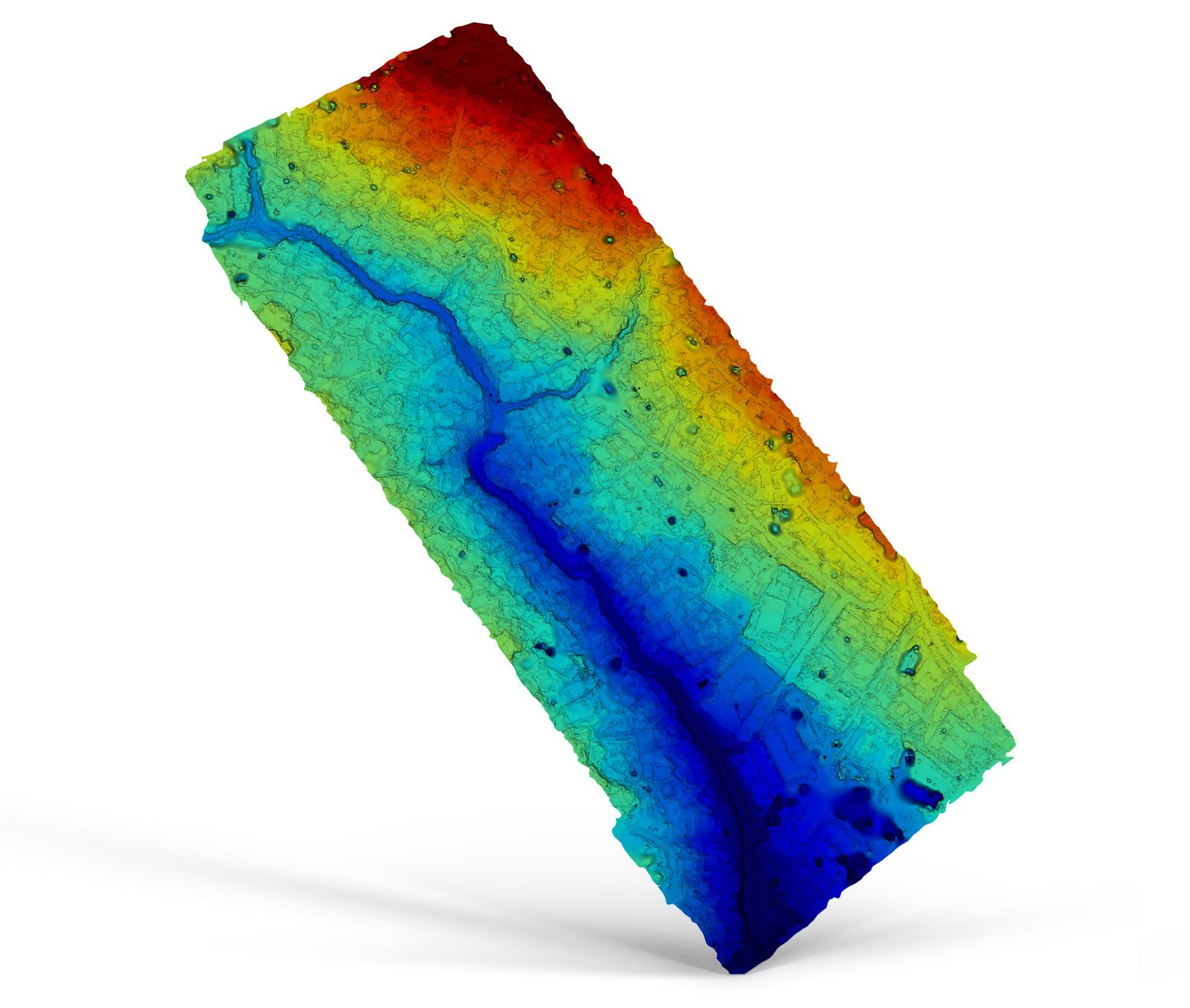
Examples of applications:
DSMs are used in agriculture to create accurate maps of crop fields, which can help farmers optimize crop yields and reduce waste.
In environmental monitoring, to track changes in land use, vegetation cover, and erosion. They can also be used to identify areas that are at risk of landslides, floods, or other natural disasters.
In archaeology, to create detailed 3D models of archaeological sites, which can help archaeologists visualize and analyze the site. DSMs can also be used to monitor changes in the site over time.
DSMs are used in geology to create detailed 3D models of geological formations, which can help geologists identify mineral deposits and other natural resources.
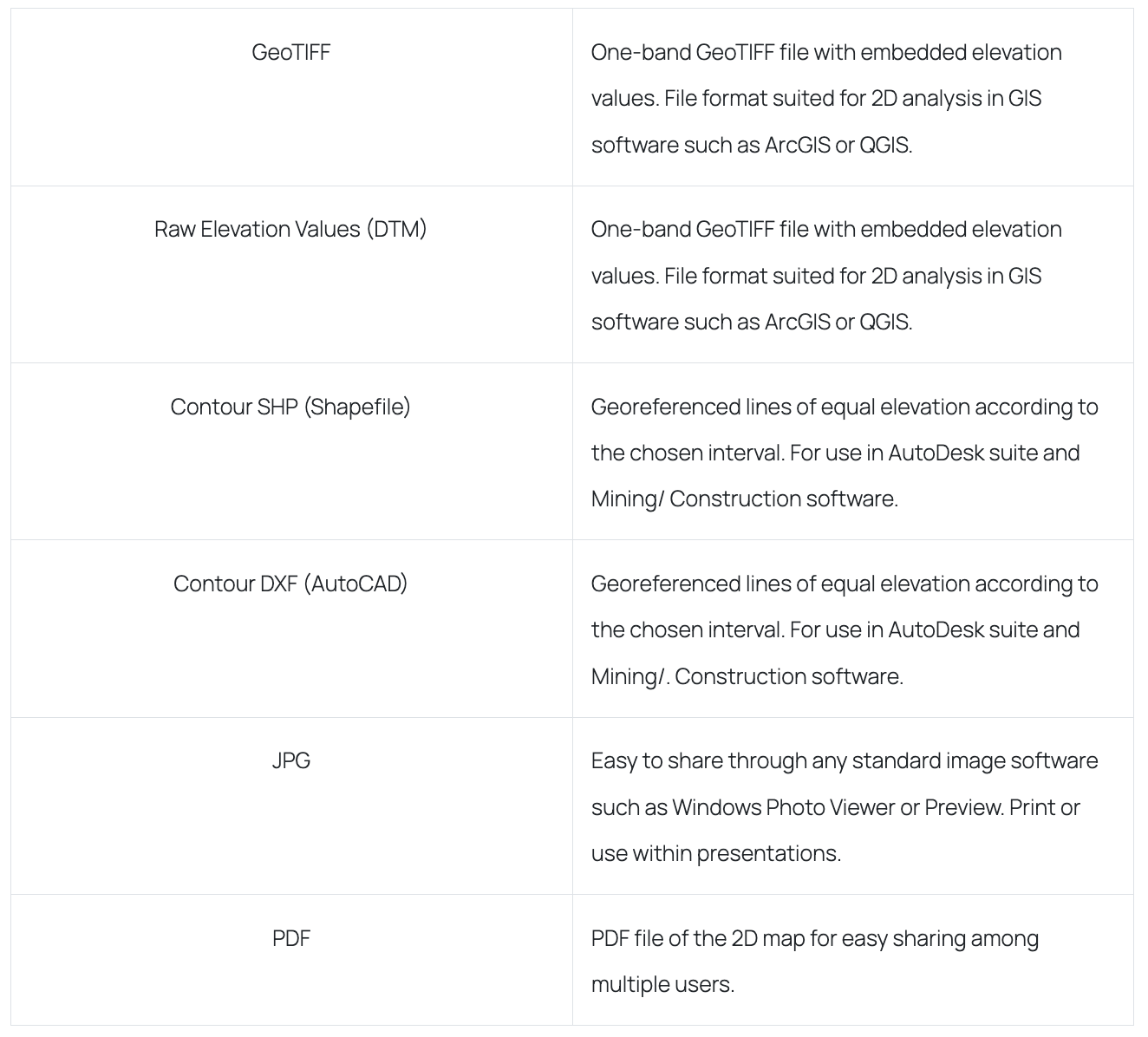
How it is delivered:
Topographic map with contour lines
Topographic maps typically display the terrain using contour lines, which are curves connecting points of equal elevation above a reference level, like the mean sea level. The contour interval in a topographic map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. High-resolution topographic maps are highly valuable for natural hazard assessment, slope stability, significant construction projects, hydrogeology, and monitoring of underground resources. Furthermore, differentiated topography resulting from surface motion is crucial in comprehending tectonic and volcanic activities and their associated hazards. The resolution of these maps can be as precise as less than 1 cm, depending on the drone's mission configuration.
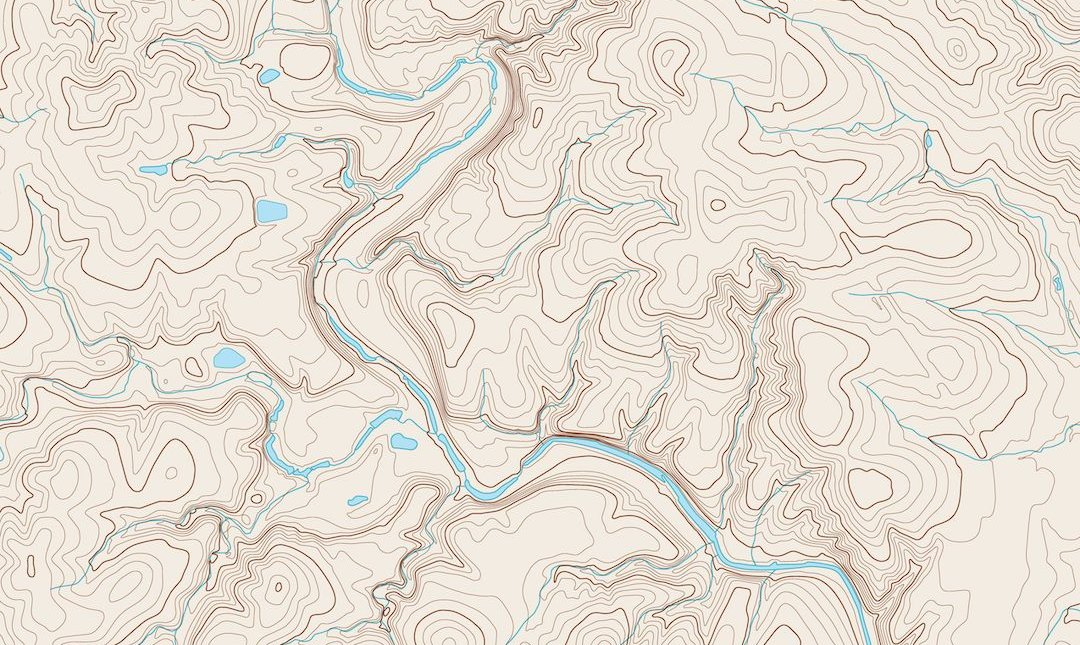
Examples of applications:
Topographic maps are used in construction projects to help determine the best location for a building, taking into account factors such as elevation, slope, and drainage.
Surveyors use topographic maps to help them locate property boundaries, determine elevations, and plan construction projects.
Topographic maps are used in emergency response situations, such as firefighting or search and rescue, to help responders navigate the terrain and locate people in need.
Mining companies use topographic maps to help identify mineral deposits and to plan the location of mining operations.
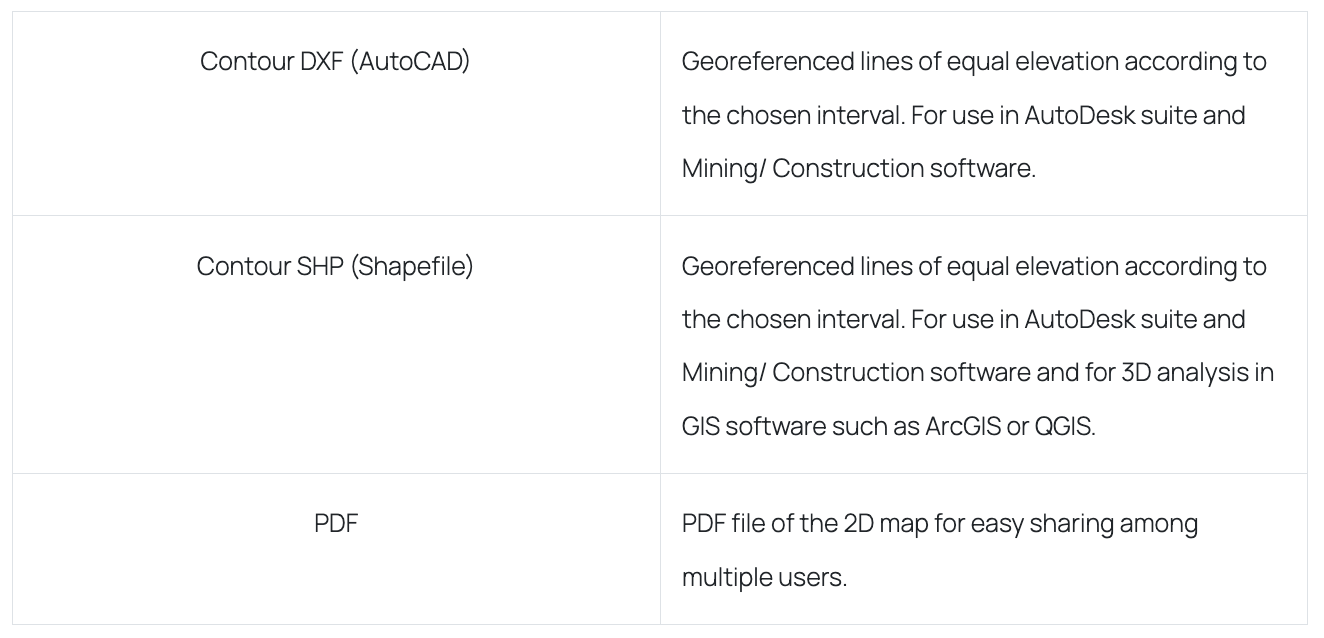
How it is delivered:
Thermal Maps
Thermal camera surveys enable the swift detection of objects with anomalous heat signatures. These types of surveys have several applications, such as identifying heat loss to improve energy efficiency, locating water leaks or moisture ingress, and identifying faults with wiring and other electrical components. Additionally, thermal surveys are particularly useful in the forestry sector, as they can identify early fire risks before they become significant threats and spread.
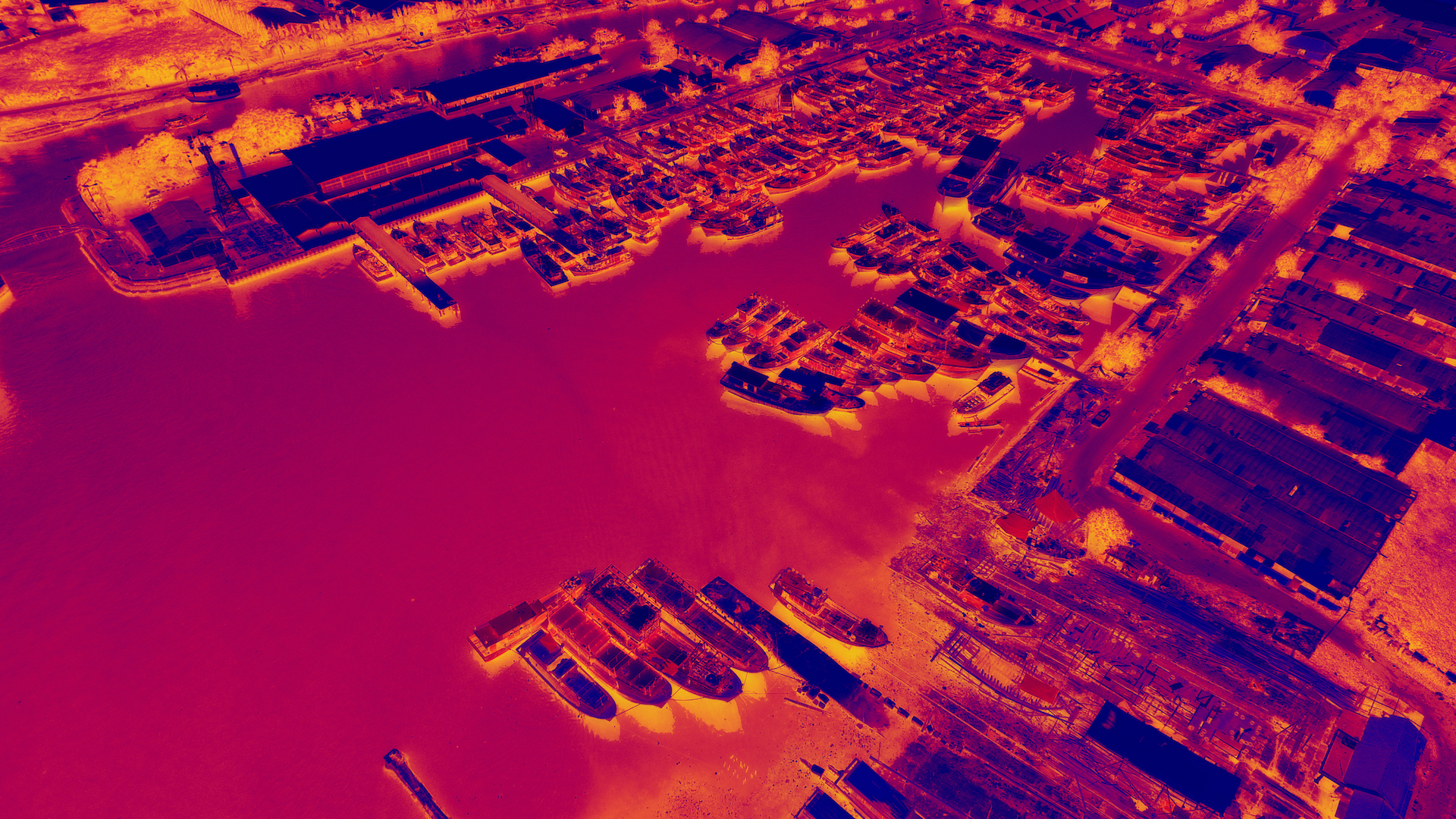

Examples of applications:
In Energy, Thermal maps can be used to identify energy leaks in buildings and improve energy efficiency. They can also be used in the detection of hotspots in power lines and electrical systems to prevent potential fires or equipment failures.
In the infrastructure industry, thermal maps can be used to detect structural issues in bridges, tunnels, and other critical infrastructure. It can also be used to identify areas of potential water leaks in pipes and other systems.
In environmental management, to monitor and detect changes in temperature in bodies of water and soil.
Thermal maps can be used in search and rescue operations to detect the heat signatures of missing persons or survivors in disaster zones.
How it is delivered:
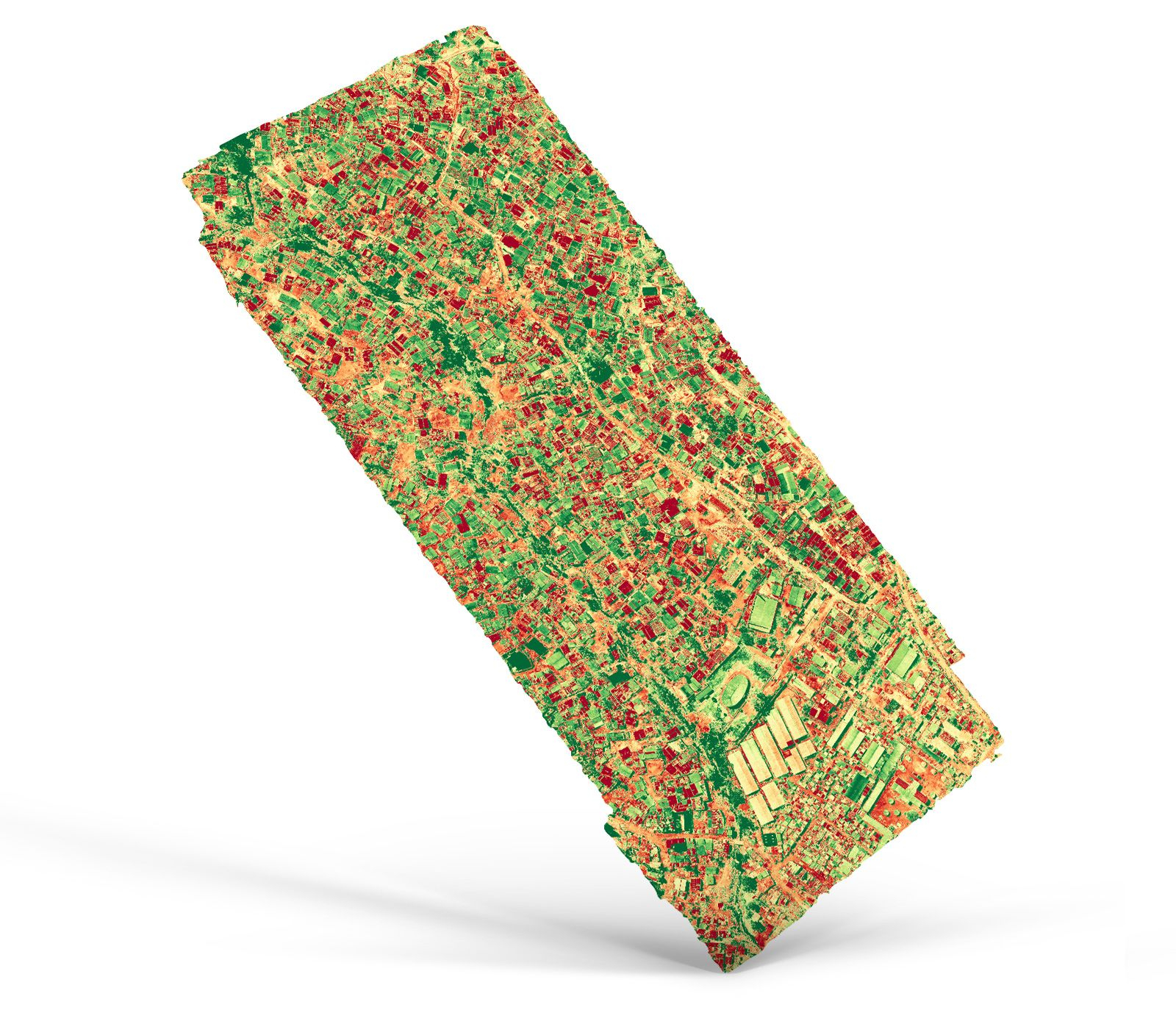
Plant health (NDVI maps)
Plant health maps provide a comprehensive analysis of agricultural data by displaying the variability within a field to determine damage and predict yields. These maps depict the area within a particular range and are created using a multi-spectral camera or NDVI algorithm, which extracts plant health data from RGB images.
Examples of applications:
Plant health maps can be used in the agriculture industry to monitor crop health and detect potential issues, such as pests, disease, or nutrient deficiencies.
In the forestry industry, plant health maps can be used to monitor forest health and detect threats, such as insect infestations or wildfire risk.
In environmental management, the use of plant health maps allows for the monitoring of ecosystem health and the detection of possible threats like habitat loss and invasive species.
In urban planning, they enable the monitoring of urban vegetation health and aid in making decisions regarding the management and development of green spaces.
How it is delivered:
Live streamed data (video footage)
It is a live video stream of what the drone is capturing during flight. This feature offers a secure, real-time video stream from the drone's perspective to team members, decision-makers, or emergency response teams.
Examples of applications:
In the construction industry, drone video footage can be used to monitor construction progress, identify potential issues, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Video footage can be used to monitor environmental changes and detect potential hazards, such as oil spills or forest fires.
In real estate, it can be used to showcase properties to potential buyers. It allows them to see the property and surrounding area from a bird's eye view.
Drones equipped with video cameras can be used in search and rescue missions to locate missing persons or survey disaster areas.
How it is delivered:
Raw data/photos
Raw images can be made available to the client for in-house processing using their proprietary software.

How it is delivered:
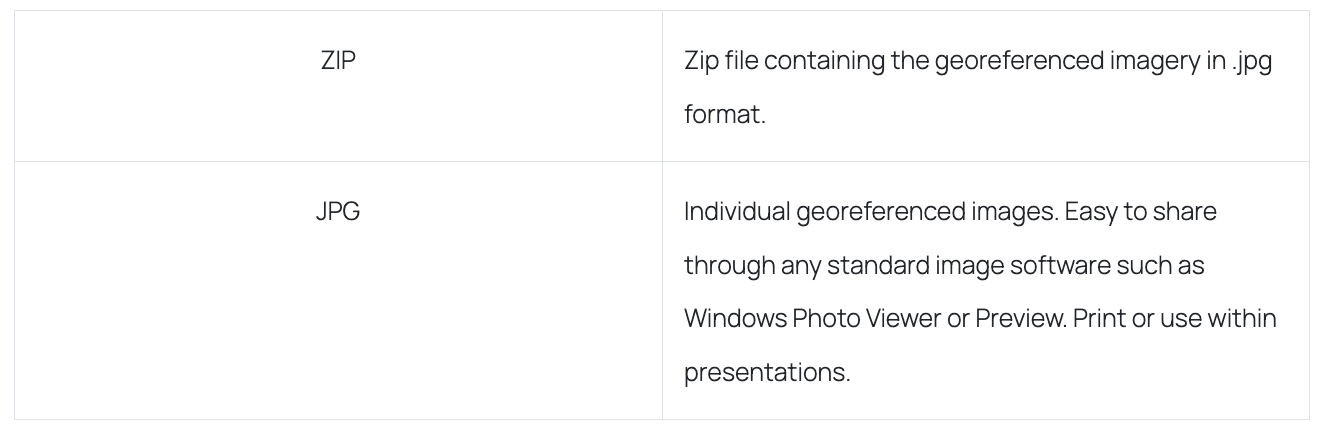
360 panoramas
A 360-degree photo is an interactive panoramic image that encompasses the original point from which the photograph was taken. This type of photo allows viewers to simulate the photographer's perspective by moving their viewpoint in any direction, including up, down, left, and right, and zooming in to view details. It is an excellent tool for exploring landscapes and gaining a comprehensive perspective from all angles.
Examples of applications:
In maritime, 360 panoramas can be used to document the condition of ships and other maritime assets. It can also be used to create virtual tours of cruise ships and other vessels.
In infrastructure, 360 panoramas can be used to document the condition of infrastructure, such as bridges, tunnels, and highways.
In construction, 360 panoramas can be used to create virtual walkthroughs of construction sites, allowing architects, contractors, and clients to get a better understanding of the project.
In the tourism industry, 360 panoramas can be used to showcase popular destinations, such as museums, landmarks, and natural attractions.
How it is delivered:

LiDAR
Lidar, short for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technique that employs pulsed laser light to measure variable distances to the Earth's surface. This technology, combined with other recorded data, generates precise three-dimensional information about the Earth's shape and surface characteristics. A lidar system comprises a laser, a scanner, and a specialized GPS receiver. Aircraft, such as airplanes and helicopters, are commonly used to gather lidar data over large areas. Topographic and bathymetric are the two types of lidar. Near-infrared lasers are commonly used in topographic lidar to map land, while green light that penetrates water is used in bathymetric lidar to measure seafloor and riverbed elevations.
Examples of applications:
In construction, LiDAR is used for accurate mapping and surveying of construction sites.
In urban planning and infrastructure development, for the creation of detailed 3D models of city landscapes.
In forestry, LiDAR can be used to measure tree heights, map forest structures, and estimate biomass.
In geological surveys and in the oil and gas industry, for exploration and monitoring of pipelines.
How it is delivered:
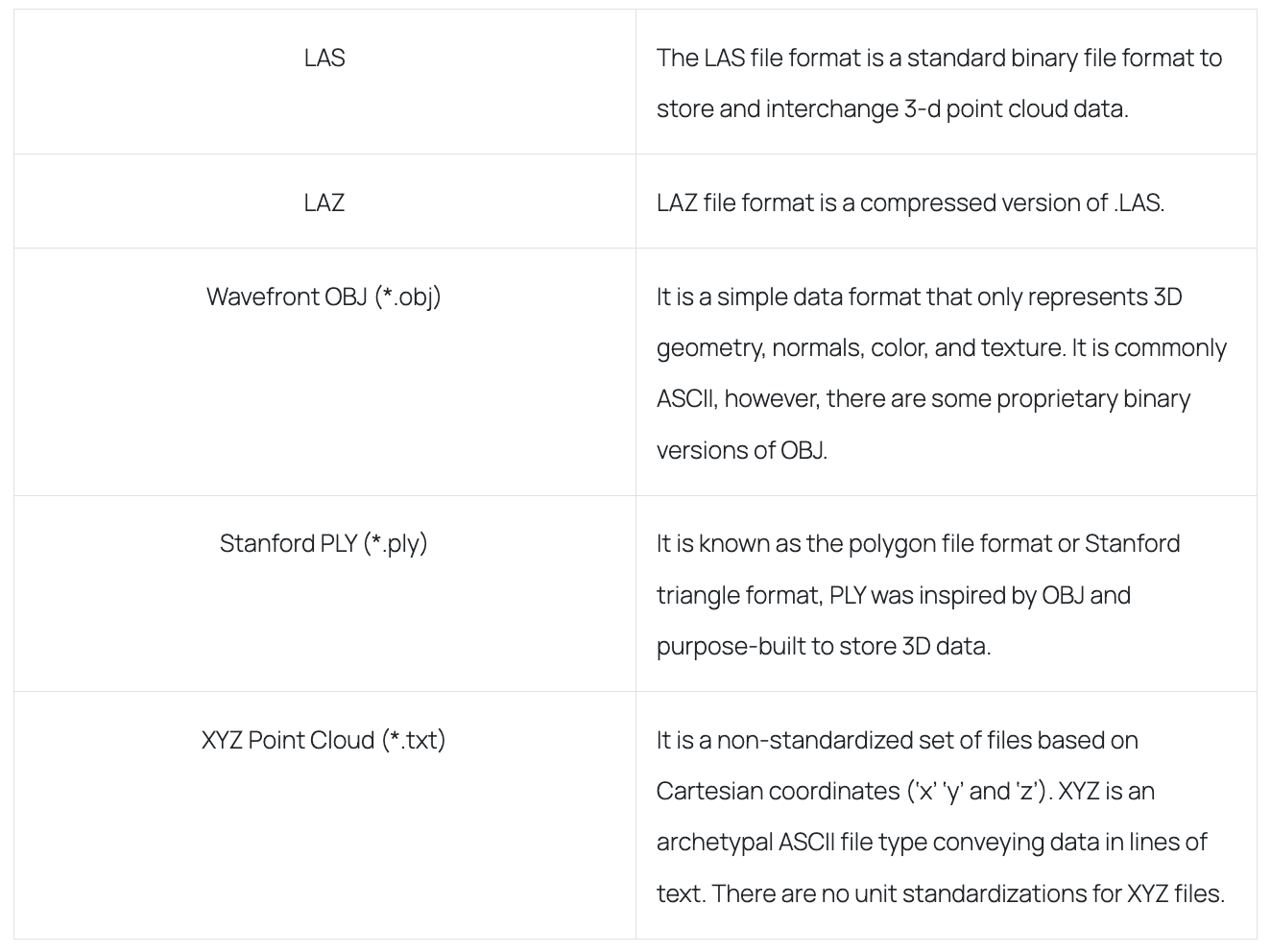
Other available file formats: ASTM E57 (*.e57), ASCII PTS (*.pts), Universal 3D (*.u3d), Topcon CL3 (*.cl3), and Autodesk DXF (*.dxf).
Conclusion
In conclusion, GLOBHE provides a range of drone data products that offer valuable insights and benefits to various industries. These products, including high-resolution aerial imagery, thermal imagery, LiDAR data, video footage, topographic maps, and digital elevation models, can help companies make more informed decisions and improve their operations.
From optimizing crop yields to improving infrastructure safety and reducing environmental risks, GLOBHE's products provide solutions that are not only effective but also sustainable. With the help of drone technology and data analytics, industries can gain a better understanding of their operations, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased safety.